The Patent That Created the Internet: How Packet-Switching Technology Revolutionized the Digital Age
The internet is so deeply woven into our daily lives that it’s hard to imagine a time before instant communication, streaming, and online shopping. But behind the modern web lies a groundbreaking patent that changed everything: packet-switching technology.

This revolutionary idea made it possible for computers to communicate efficiently, enabling the internet to grow from a niche government experiment into a global necessity. But how did it all begin? And why does packet-switching remain one of the most important inventions in history?
Let’s explore the origins, impact, and future of the technology that powers our digital world.
The Birth of a Digital Revolution: The Origins of the Internet
Before the internet, communication was linear and centralized. Messages were sent via telephone lines, radio waves, or postal mail, all of which had significant limitations in speed, reliability, and efficiency.
In the 1960s, scientists and engineers began asking: What if we could break data into smaller parts and send them independently?
This question led to the invention of packet-switching technology—a breakthrough that transformed how computers talk to each other.

Key Innovators and Their Vision
- Paul Baran (RAND Corporation) – Proposed a decentralized communication network for the U.S. military to survive nuclear attacks.
- Donald Davies (National Physical Laboratory, UK) – Coined the term packet switching and developed the first working model.
- Leonard Kleinrock (MIT/UCLA) – Created the mathematical theory behind packet-switching networks.
- Vint Cerf & Bob Kahn (DARPA) – Developed TCP/IP, the foundation of modern internet communication.
Their collective work laid the foundation for the modern internet, proving that breaking data into packets and transmitting them separately was far more efficient than traditional methods.
Breaking Down Packet-Switching: The Technology That Made the Internet Possible
So, what exactly is packet-switching, and why was it such a breakthrough?

How Packet-Switching Works
Instead of sending data as one continuous stream, packet-switching breaks it into small, independent packets. Each packet:
✔ Travels separately through different routes across the network
✔ Reassembles at the destination in the correct order
✔ Increases efficiency by using the fastest available path
Why It Was Revolutionary
- Redundancy – If one route fails, packets are rerouted, ensuring high reliability.
- Efficiency – Multiple users can send data simultaneously without network congestion.
- Scalability – Unlike older centralized systems, packet-switching allows networks to grow indefinitely.
Before packet-switching, circuit-switching (like in telephone networks) required a dedicated connection for each communication, which wasted bandwidth and limited users. Packet-switching eliminated this bottleneck, paving the way for the internet to scale globally.
📌 By 1993, the internet carried only 1% of global communications. By 2000, that number had skyrocketed to 51%.
The Fundamental Patents Behind the Internet
The rise of the internet was fueled by several key patents that shaped modern networking.
1️⃣ The Packet-Switching Patent (Filed in 1961)
- Introduced the concept of breaking data into packets
- Provided a more resilient network structure
- Became the core of modern internet communication
2️⃣ TCP/IP Protocol Patent (Developed in the 1970s)
- Enabled seamless communication between different computer networks
- Allowed for the creation of the World Wide Web
- Became the universal standard for internet data transfer
3️⃣ Network Architecture Patents
- Defined how routers and servers direct internet traffic
- Created the backbone for global connectivity
- Supported the development of modern cloud computing
These patents set the stage for high-speed data transmission, real-time communication, and the digital economy we rely on today.
How Packet-Switching Transformed Communication Forever
Imagine a world without instant messaging, video calls, or online banking. None of these would be possible without packet-switching.

Key Milestones in Internet History
📅 1969 – ARPANET (the first internet prototype) successfully transmits a message using packet-switching.
📅 1972 – The first email is sent, revolutionizing communication.
📅 1991 – The World Wide Web is invented, making the internet accessible to the public.
📅 2000s–Present – Internet speeds increase from 56 kbps dial-up to over 1 Gbps fiber-optic connections.
📌 By 2019, global networks were transmitting data at speeds up to 800 Gbit/s, a direct result of packet-switching innovations.
The Economic Impact of Internet Technology Patents
The internet’s economic footprint is staggering.
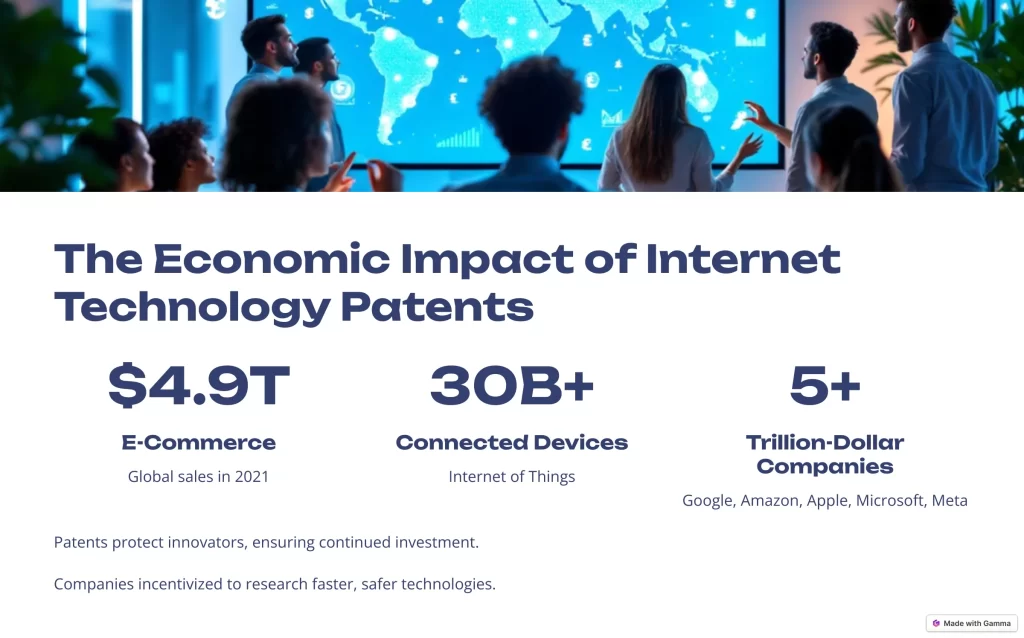
- $4.9 trillion in global e-commerce sales (2021) 📈
- Over 30 billion devices connected to the internet
- The rise of trillion-dollar tech companies (Google, Amazon, Apple, Microsoft, etc.)
Why Internet Patents Matter Today
Patents protect innovators, ensuring continued investment in faster, safer, and smarter internet technologies. Without patent protection, tech companies would have little incentive to invest in groundbreaking research.
Modern Applications of Packet-Switching Patents

🔹 Social Media – Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and TikTok rely on packet-switching for instant sharing.
🔹 Streaming Services – Netflix and YouTube deliver videos in data packets, reducing buffering.
🔹 Cloud Computing – Google Drive, Dropbox, and AWS use packet-switching for fast and secure data transfers.
🔹 Cryptocurrency & Blockchain – Secure transactions are validated and sent via packet-switched networks.
Final Thoughts: The Lasting Legacy of Internet Patents
The invention of packet-switching technology wasn’t just a breakthrough—it was the foundation of the digital age.
🔹 Without it, we wouldn’t have the internet, social media, or modern digital economies.
🔹 Its impact spans communication, business, entertainment, and global connectivity.
🔹 Future innovations—like 6G, quantum networking, and AI-driven infrastructure—will continue to build on this foundation.
Every time you send an email, stream a video, or join a Zoom call, you’re benefiting from the brilliant minds who revolutionized the way we communicate.
💡 So, what’s next? Could the next internet breakthrough be happening right now?
FAQ: Understanding the Internet’s Origins
Who invented packet-switching technology?
Paul Baran, Donald Davies, and Leonard Kleinrock were the pioneers of packet-switching, with additional contributions from Vint Cerf and Bob Kahn.
Why is packet-switching better than circuit-switching?
Packet-switching optimizes bandwidth, prevents congestion, and allows multiple users to share the network simultaneously—unlike traditional circuit-switching, which requires a dedicated line.
Is packet-switching still relevant today?
Absolutely! Every online service—cloud computing, 5G, IoT, and AI-driven networks—still depends on packet-switching for efficient data transmission.
How do patents affect internet innovation?
Patents protect breakthroughs in networking, encouraging ongoing investment in faster, safer, and more advanced internet technologies.
What Do You Think?
How do you see internet technology evolving in the next decade? Will new patents revolutionize digital communication even further?
Share your thoughts below! 🚀






